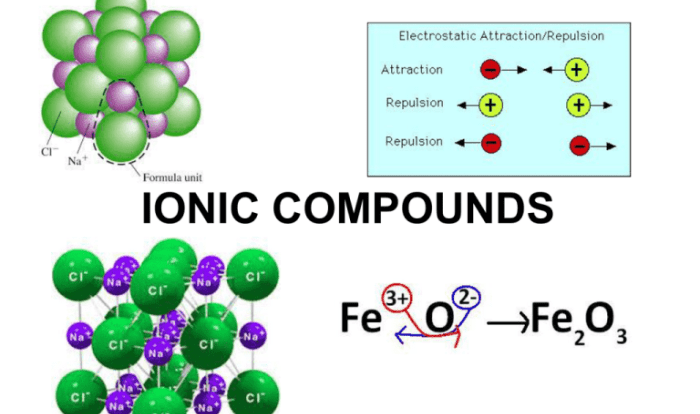
The Mendeleev Lab of 1869 Answer Key unlocks the door to a scientific revolution, providing a comprehensive guide to Dmitri Mendeleev’s groundbreaking work that shaped our understanding of the elements and their properties. This key offers a detailed examination of Mendeleev’s periodic table, revealing the significance of his groundbreaking discoveries and their lasting impact on the field of chemistry.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Mendeleev’s periodic table, published in 1869, marked a significant advancement in the field of chemistry. It organized the known elements based on their atomic weights and chemical properties, leading to the development of a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements.
Key features and innovations introduced by Mendeleev in his periodic table include:
Organization of Elements
- Mendeleev arranged the elements in ascending order of atomic weight.
- Elements with similar chemical properties were grouped together in vertical columns, known as groups.
- Horizontal rows, called periods, represented increasing atomic weight.
Periodic Law
Mendeleev proposed the periodic law, which states that the chemical and physical properties of elements vary periodically with their atomic weights.
Prediction of New Elements
Based on the periodic table, Mendeleev predicted the existence of several new elements, including gallium, scandium, and germanium. These predictions were later confirmed by the discovery of these elements.
Revisions and Improvements
Mendeleev’s periodic table has undergone revisions and improvements over time as new elements were discovered and the understanding of atomic structure advanced.
Elements and Properties: The Mendeleev Lab Of 1869 Answer Key
Mendeleev’s 1869 periodic table included 63 known elements, organized based on their atomic masses and chemical properties. This organization revealed patterns in the elements’ properties, allowing Mendeleev to predict the existence and properties of yet-undiscovered elements.
Organization of Elements
Mendeleev arranged the elements in his table in order of increasing atomic mass, from lightest to heaviest. He then grouped elements with similar chemical properties into vertical columns, known as groups. Horizontal rows, called periods, contained elements with increasing atomic numbers.
By organizing the elements in this way, Mendeleev identified periodic trends in their properties. For example, elements in the same group typically have similar valence electrons, which determine their chemical reactivity. Elements in the same period generally have the same number of electron shells.
Table of Elements
| Group | Period 1 | Period 2 | Period 3 | Period 4 | Period 5 | Period 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | H | Li | Na | K | Rb | Cs |
| II | Be | Mg | Ca | Sr | Ba | |
| III | B | Al | Ga | In | Tl | |
| IV | C | Si | Ge | Sn | Pb | |
| V | N | P | As | Sb | Bi | |
| VI | O | S | Se | Te | Po | |
| VII | F | Cl | Br | I |
Groupings and Trends
Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table based on their atomic masses and chemical properties. He grouped elements with similar properties into vertical columns, known as groups or families. The elements in a group share similar valence electron configurations, which determines their chemical reactivity.
Periodic Trends
Mendeleev also observed trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements across periods and groups. These trends are a result of the increasing atomic number and the corresponding changes in the electronic structure of the elements.
- Across a period (horizontal row):As you move from left to right across a period, the atomic number increases, and the number of valence electrons increases. This results in a gradual increase in metallic character and a decrease in non-metallic character.
- Down a group (vertical column):As you move down a group, the atomic number increases, and the number of electron shells increases. This results in a gradual increase in atomic radius, ionic radius, and metallic character.
Prediction of New Elements
Mendeleev’s periodic table had several gaps, indicating the existence of undiscovered elements. Based on these gaps, he predicted the properties of these missing elements.
Discovery of New Elements
Mendeleev’s predictions were remarkably accurate. Several elements were later discovered that matched his predictions, confirming the validity of his periodic table.
- Gallium (Ga): Mendeleev predicted an element called “eka-aluminum” with properties similar to aluminum. Gallium, discovered in 1875, fit these predictions.
- Scandium (Sc): Mendeleev predicted an element called “eka-boron” with properties similar to boron. Scandium, discovered in 1879, fit these predictions.
- Germanium (Ge): Mendeleev predicted an element called “eka-silicon” with properties similar to silicon. Germanium, discovered in 1886, fit these predictions.
Evolution of the Periodic Table
The periodic table has undergone significant evolution since Mendeleev’s initial proposal in 1869. Over time, scientists have refined and expanded the table, leading to a deeper understanding of the chemical elements and their properties.
One major contribution was made by Henry Moseley in 1913, who discovered that the atomic number, rather than atomic mass, was the fundamental property that determined an element’s position on the periodic table. This discovery led to a more accurate organization of the elements and the correction of several errors in Mendeleev’s original table.
Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table is a result of the collective efforts of numerous scientists and is based on the principles of atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical reactivity. It is organized into 18 vertical columns, known as groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods.
Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to the same number of valence electrons, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Advancements
The periodic table has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of chemistry and has played a crucial role in the development of new technologies and materials. It continues to be an essential tool for chemists, physicists, and other scientists, providing a comprehensive overview of the chemical elements and their properties.
Applications and Impact
Mendeleev’s periodic table has found widespread applications in various scientific fields, revolutionizing our understanding of chemical reactions and the development of new materials.
Understanding Chemical Reactions, The mendeleev lab of 1869 answer key
The periodic table provides a framework for understanding the chemical properties of elements. By organizing elements based on their atomic number, it allows scientists to predict the reactivity and behavior of elements in chemical reactions. This knowledge has been instrumental in developing new chemical processes, synthesizing new compounds, and understanding the interactions between different elements.
Development of New Materials
The periodic table has played a crucial role in the development of new materials with tailored properties. By understanding the relationships between the properties of elements and their position in the table, scientists can design and synthesize materials with specific characteristics.
This has led to the development of advanced materials for applications in electronics, energy storage, medicine, and other industries.
Prediction of New Elements
One of the most remarkable applications of the periodic table is its ability to predict the existence of new elements. Mendeleev himself predicted the existence of several elements, including gallium, scandium, and germanium, based on the gaps in his periodic table.
This predictive power has guided the search for new elements and has contributed to the expansion of the periodic table over time.
Education and Research
The periodic table is an indispensable tool in chemistry education and research. It provides a visual representation of the elements and their properties, making it easier for students to understand the fundamental principles of chemistry. It also serves as a reference for researchers, helping them to identify and compare the properties of different elements.
Quick FAQs
What was the significance of Mendeleev’s 1869 periodic table?
Mendeleev’s 1869 periodic table was a groundbreaking achievement that organized the known elements based on their atomic masses and chemical properties, revealing patterns and trends that had not been previously recognized.
How did Mendeleev predict the existence of new elements?
Mendeleev’s periodic table left gaps for undiscovered elements, based on the patterns he observed in the properties of the known elements. His predictions were later confirmed with the discovery of elements such as gallium, scandium, and germanium.
What are some of the practical applications of Mendeleev’s periodic table?
Mendeleev’s periodic table has numerous practical applications, including the prediction of chemical reactions, the development of new materials, and the classification of elements for various industrial and scientific purposes.