Delving into the depths of biochemistry, we present the macromolecule comparison table answers key, an indispensable tool for understanding the fundamental building blocks of life. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate world of macromolecules, providing a structured framework for comparing their diverse properties and functions.
As we embark on this scientific exploration, we will dissect the chemical composition, structural characteristics, and biological significance of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Through the lens of a comparative table, we will uncover the intricate relationships between these macromolecules, revealing their interconnected roles in sustaining life’s intricate tapestry.
Types of Macromolecules: Macromolecule Comparison Table Answers Key
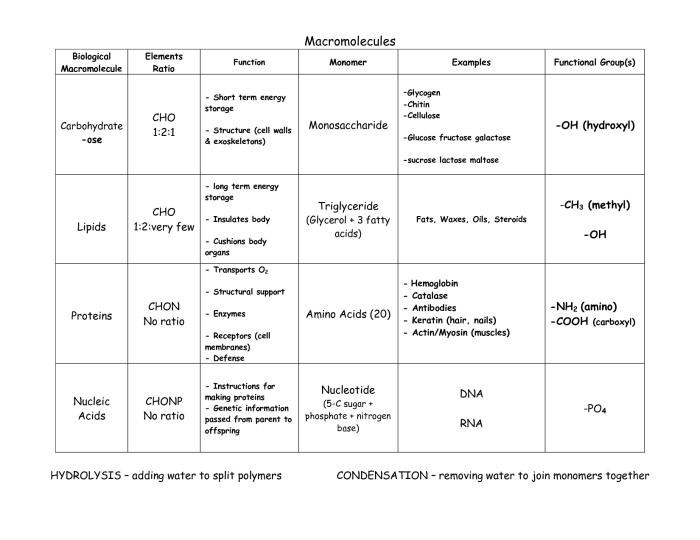
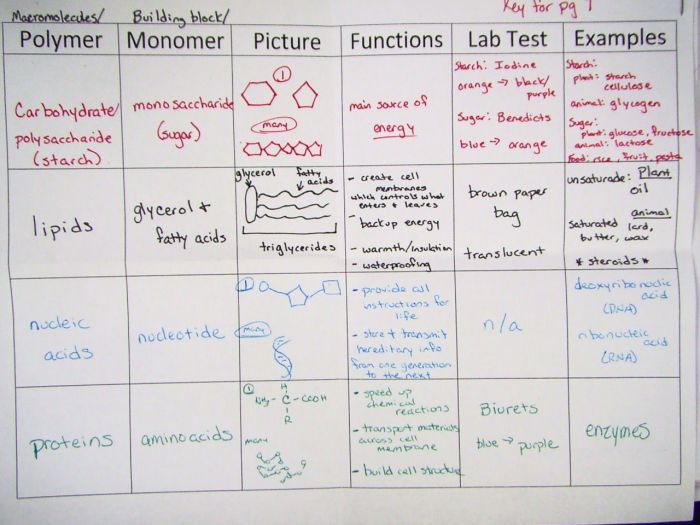
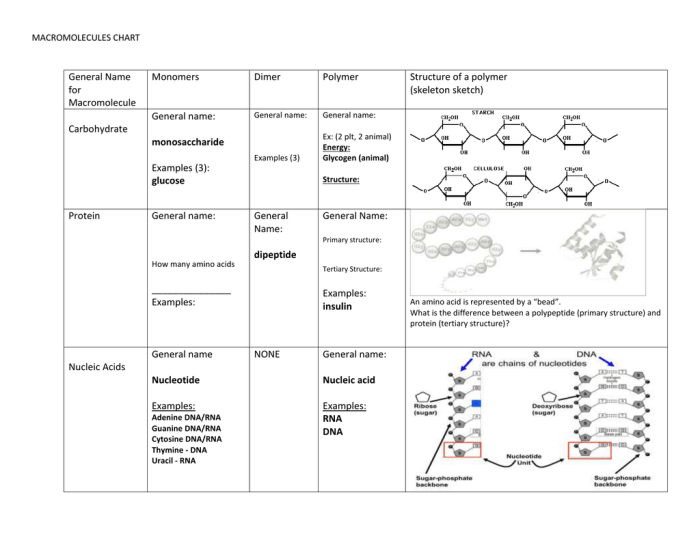
Macromolecules are large molecules that are essential for life. They are composed of thousands or even millions of atoms and can have a molecular weight of up to several million daltons. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.Carbohydrates
are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are the body’s main source of energy and are classified into three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose. Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides linked together, such as sucrose and lactose.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of many monosaccharides linked together, such as starch and cellulose.Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. They are the building blocks of cells and tissues and are responsible for a wide range of functions, including metabolism, growth, and repair.
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in different ways to create a vast array of proteins.Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
They are insoluble in water and are used for energy storage, insulation, and waterproofing. Lipids include fats, oils, and waxes. Fats and oils are made up of fatty acids, which are long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached.
Waxes are made up of fatty acids and alcohols.Nucleic acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms. They are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic material of cells and is made up of two strands of nucleotides linked together by hydrogen bonds.
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of a macromolecule comparison table?
A macromolecule comparison table provides a structured overview of the different types of macromolecules, their chemical composition, structural characteristics, and biological functions, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of their diverse roles in living organisms.
How can I use the macromolecule comparison table answers key?
The macromolecule comparison table answers key serves as a reference guide, allowing you to quickly access information about specific macromolecules, compare their properties, and deepen your understanding of their biological significance.
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each type possesses distinct chemical compositions, structural features, and functions, contributing to the diverse processes and structures found in living organisms.