Which of the following is true about calcium homeostasis? This intriguing question unveils the critical role of calcium ions in orchestrating diverse cellular processes and maintaining tissue-specific functions. Calcium homeostasis, the intricate balance of calcium levels within cells and tissues, is a fundamental aspect of biological systems, with disruptions leading to a cascade of physiological consequences.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the mechanisms governing calcium homeostasis, examining the interplay of calcium pumps, channels, and exchangers. We will uncover how hormones and second messengers exert their influence on calcium dynamics, shaping cellular responses and signaling pathways. Furthermore, we will explore the tissue-specific adaptations of calcium homeostasis, highlighting the unique mechanisms employed by bone, muscle, and neurons to maintain optimal calcium levels.
1. Calcium Homeostasis Overview

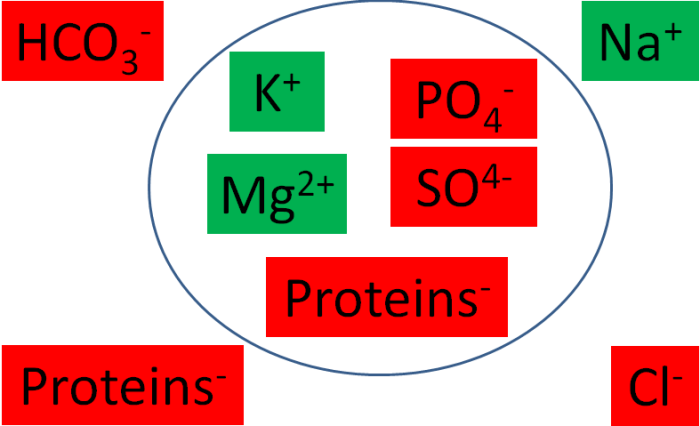
Calcium homeostasis is crucial for the proper functioning of biological systems. Calcium ions (Ca2+) play a vital role in various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, enzyme activity, and bone formation.
Disruptions in calcium homeostasis can lead to a wide range of physiological abnormalities, including muscle weakness, cardiac arrhythmias, and neurological disorders.
Regulation of Calcium Levels, Which of the following is true about calcium homeostasis
The regulation of calcium levels within cells is a complex process involving a coordinated interplay of calcium pumps, channels, and exchangers. Calcium pumps, such as the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) in muscle cells, actively transport calcium ions out of the cytosol into intracellular stores.
Calcium channels, such as voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), allow the influx of calcium ions into the cytosol from the extracellular space or intracellular stores. Calcium exchangers, such as the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX), facilitate the exchange of calcium ions with sodium ions across the plasma membrane.
Hormones and second messengers, such as parathyroid hormone (PTH) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), play a crucial role in regulating calcium homeostasis by modulating the activity of calcium pumps, channels, and exchangers.
General Inquiries: Which Of The Following Is True About Calcium Homeostasis
What is the significance of calcium homeostasis?
Calcium homeostasis ensures optimal calcium levels within cells and tissues, supporting essential cellular processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and hormone secretion.
How is calcium homeostasis regulated?
Calcium homeostasis is regulated by a complex interplay of calcium pumps, channels, and exchangers, which work together to maintain a delicate balance of calcium influx and efflux.
What are the clinical implications of disruptions in calcium homeostasis?
Disruptions in calcium homeostasis can lead to a range of clinical conditions, including hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) and hypercalcemia (high calcium levels), which can manifest with symptoms such as muscle weakness, seizures, and bone abnormalities.