Unit chemical bonding forming ionic compounds ws 2 – Unit chemical bonding, exemplified in the formation of ionic compounds like WS2, plays a crucial role in shaping the properties and applications of various materials. This article delves into the process of ionic bond formation, the characteristics of ionic compounds, and the significance of WS2 in this context.
Ionic Bonding Formation

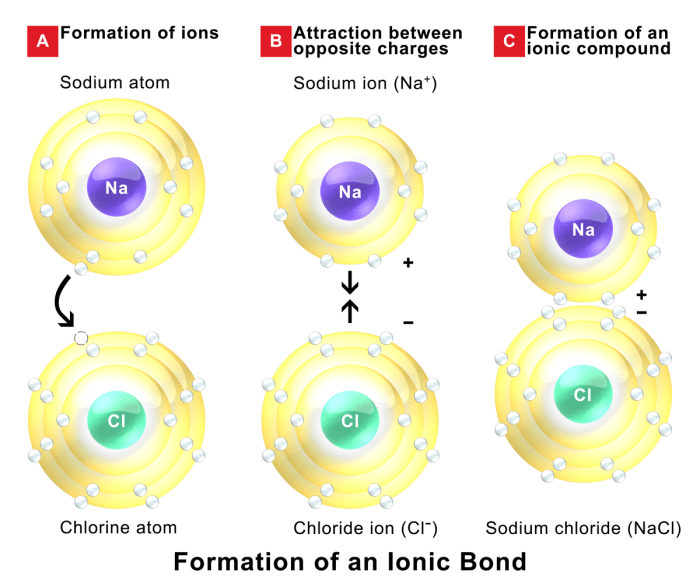
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond formed between two oppositely charged ions. It occurs when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, creating a positive ion (cation) and a negative ion (anion). The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds the compound together.
For example, sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) can form an ionic compound, sodium chloride (NaCl). Sodium has one valence electron, which it is willing to lose, while chlorine has seven valence electrons and needs one more to complete its valence shell.
When sodium loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged sodium ion (Na+), and when chlorine gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). The electrostatic attraction between the Na+ and Cl- ions holds the NaCl compound together.
Unit Chemical Bonding
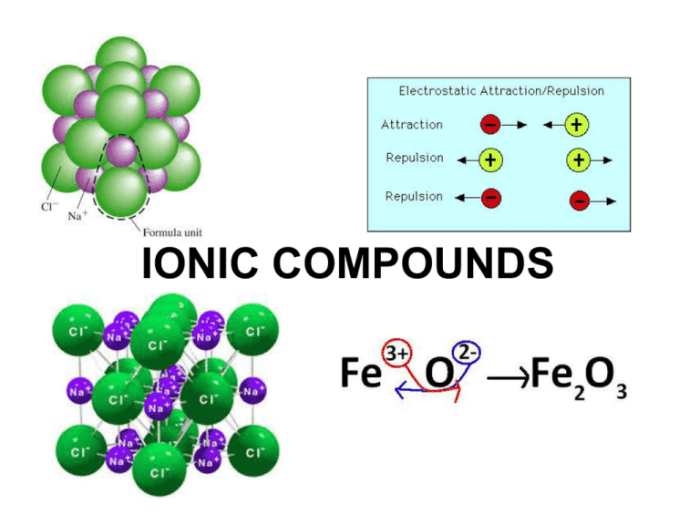
Unit chemical bonding is the smallest unit of a compound that retains the chemical properties of the compound. In ionic compounds, the unit chemical bonding is the formula unit, which is the simplest whole-number ratio of the ions in the compound.
For example, the formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) is 1:1, meaning that there is one sodium ion for every one chloride ion in the compound.
WS2

WS 2is a transition metal dichalcogenide with a layered structure. Each layer consists of a sheet of tungsten (W) atoms sandwiched between two sheets of sulfur (S) atoms. The W atoms are in the +4 oxidation state, and the S atoms are in the -2 oxidation state.
WS 2can form ionic compounds with a variety of other elements. For example, it can form WS 2Cl 2with chlorine and WS 2O 3with oxygen.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds are typically solids at room temperature.
- They have high melting and boiling points.
- They are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted.
- They are soluble in polar solvents, such as water.
- They are generally brittle.
The properties of ionic compounds are influenced by the strength of the ionic bond. The stronger the ionic bond, the higher the melting and boiling points, and the lower the solubility.
Applications of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have a wide variety of applications, including:
- Table salt (NaCl) is used as a food seasoning and preservative.
- Baking soda (NaHCO 3) is used as a leavening agent in baking.
- Calcium chloride (CaCl 2) is used as a deicing agent.
- Potassium iodide (KI) is used as a supplement to prevent iodine deficiency.
- Ionic liquids are used as solvents in a variety of industrial processes.
Ionic compounds are essential to many industries, including the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
Essential FAQs: Unit Chemical Bonding Forming Ionic Compounds Ws 2
What is the process of ionic bond formation?
Ionic bond formation occurs when atoms transfer electrons to achieve stable electron configurations, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
How does WS2 form ionic compounds?
WS2 forms ionic compounds by transferring electrons from tungsten (W) atoms to sulfur (S) atoms, creating W2+ cations and S2- anions, which are held together by electrostatic attraction.
What are the key properties of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds typically exhibit high melting and boiling points, solubility in polar solvents, and the ability to conduct electricity when dissolved or molten.