When titrating inspired oxygen which arterial oxyhemoglobin – When titrating inspired oxygen, which arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation is a critical consideration. Understanding the relationship between inspired oxygen and arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation is essential for optimizing patient care and preventing complications.
This comprehensive guide explores the physiological effects of inspired oxygen, methods for titration, considerations for titration, clinical applications, and potential complications. It provides a detailed overview of the topic, empowering healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding oxygen therapy.
Titrating Inspired Oxygen: Considerations and Implications: When Titrating Inspired Oxygen Which Arterial Oxyhemoglobin

Titration of inspired oxygen involves adjusting the concentration of oxygen delivered to a patient to maintain adequate oxygenation. This process plays a crucial role in managing respiratory conditions and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Physiological Effects of Inspired Oxygen
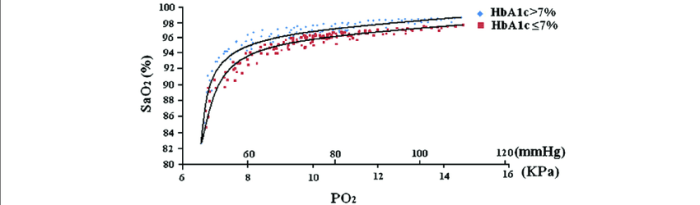
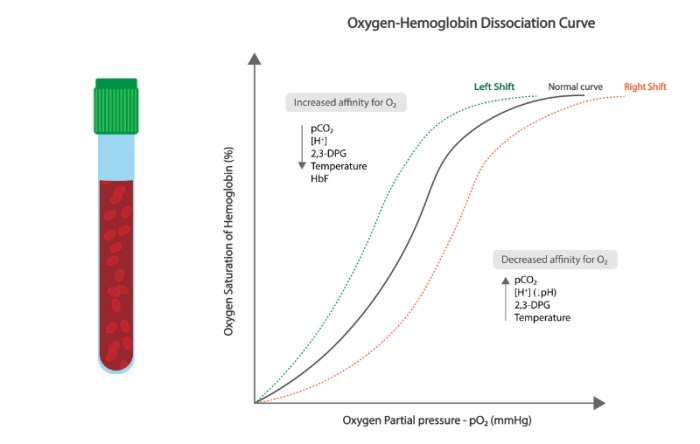
Varying inspired oxygen concentrations directly impact arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation (SaO2). Higher inspired oxygen levels lead to increased PaO2 and SpO2, indicating improved oxygenation. The oxygen dissociation curve illustrates the relationship between PaO2 and SaO2, demonstrating the nonlinear nature of oxygen binding to hemoglobin.
Methods for Titrating Inspired Oxygen, When titrating inspired oxygen which arterial oxyhemoglobin
Several techniques are used to titrate inspired oxygen, including:
- Oxygen Masks:Deliver a fixed concentration of oxygen, ranging from 24% to 100%.
- Nasal Cannulas:Provide a lower concentration of oxygen (24-40%) and are typically used for patients with mild hypoxemia.
- Mechanical Ventilators:Offer precise control over inspired oxygen concentration and can be used for patients with severe respiratory failure.
Considerations for Titration
When determining the appropriate inspired oxygen concentration, factors to consider include:
- Patient-Specific Factors:Age, underlying medical conditions, and respiratory status influence oxygenation needs.
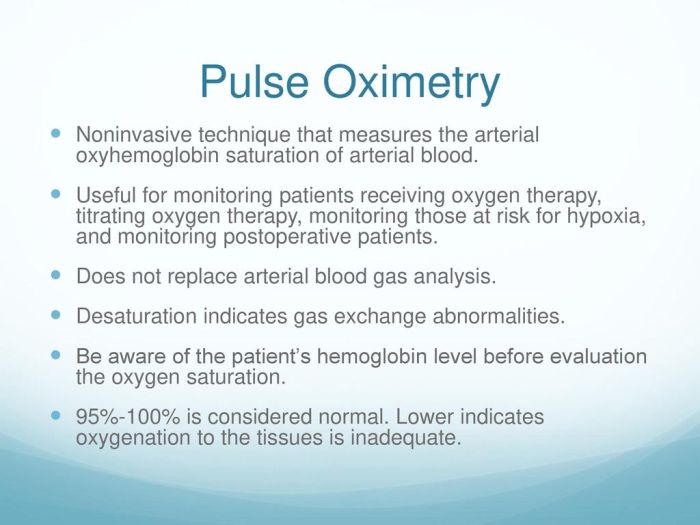
- Pulse Oximetry:Non-invasive monitoring of SpO2 provides real-time feedback on oxygenation.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis:Measures PaO2 and SaO2, offering a more precise assessment of oxygenation.
Clinical Applications of Titration
Titration of inspired oxygen is essential in various clinical scenarios:
- COPD:Optimizing oxygenation improves exercise tolerance and reduces exacerbations.
- ARDS:Titrating inspired oxygen to target PaO2 levels helps prevent both hypoxemia and hyperoxia.
Complications of Oxygen Titration
Excessive inspired oxygen can lead to complications:
- Hyperoxia:High PaO2 levels can cause oxygen toxicity and oxidative stress.
- Retinopathy of Prematurity:In neonates, excessive oxygen exposure can damage retinal blood vessels.
FAQ
What is the purpose of titrating inspired oxygen?
Titrating inspired oxygen aims to maintain adequate arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation while avoiding hyperoxia and its associated complications.
How is inspired oxygen titrated?
Inspired oxygen can be titrated using various methods, including oxygen masks, nasal cannulas, and mechanical ventilators. The choice of method depends on the patient’s condition and oxygen requirements.
What factors should be considered when titrating inspired oxygen?
Factors to consider include the patient’s age, underlying medical conditions, respiratory status, and pulse oximetry readings.