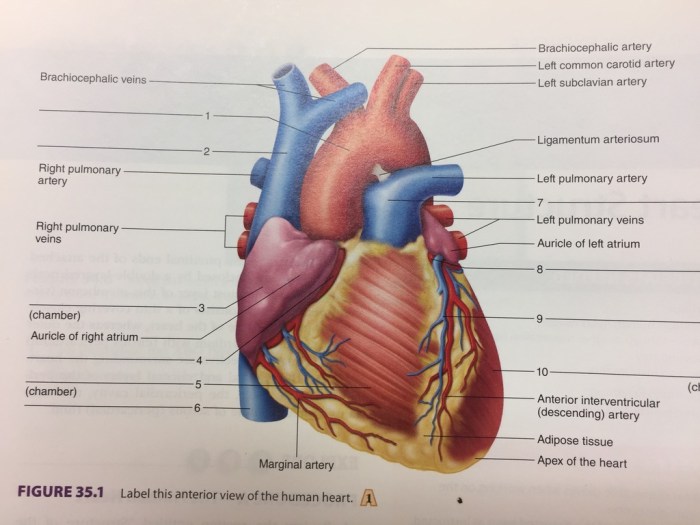
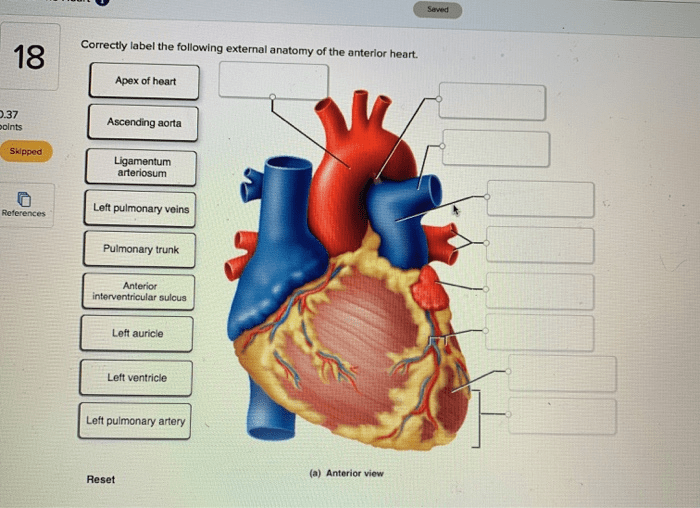
Correctly label the following external anatomy of the anterior heart. – Correctly labeling the external anatomy of the anterior heart is essential for understanding its structure and function. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key anatomical landmarks and structures visible on the anterior surface of the heart, enabling accurate identification and comprehension.
The anterior heart, located in the mediastinum, comprises the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. These chambers are responsible for receiving and pumping blood throughout the body.
Anatomical Overview of the Anterior Heart
The anterior heart is the front surface of the heart, which is located in the mediastinum, the middle compartment of the thoracic cavity. It is positioned slightly to the left of the midline and is oriented obliquely, with the apex pointing inferiorly and to the left.
The anterior surface is bounded by the sternum anteriorly and the pericardium posteriorly.
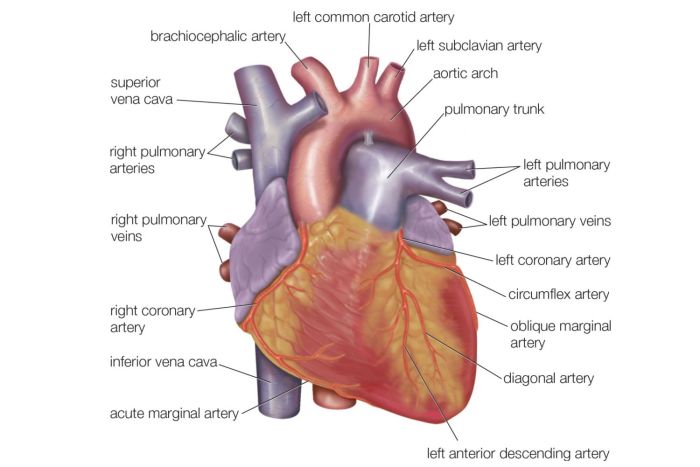
Key anatomical landmarks on the anterior surface include the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle, pulmonary artery, aorta, and superior vena cava. These structures are separated by grooves, such as the atrioventricular groove and the interventricular groove.
Identification of External Structures, Correctly label the following external anatomy of the anterior heart.
The right atrium is located in the upper right quadrant of the anterior heart. It is a thin-walled structure that receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. The right ventricle is located below and to the right of the right atrium.
It is a thick-walled structure that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
The left atrium is located in the upper left quadrant of the anterior heart. It is a thin-walled structure that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. The left ventricle is located below and to the left of the left atrium.
It is a thick-walled structure that pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Major Vessels and Associated Structures
The pulmonary artery arises from the right ventricle and carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs. It is located superior to the aorta and runs along the left border of the heart. The aorta arises from the left ventricle and carries oxygenated blood to the body.
It is located inferior to the pulmonary artery and runs along the right border of the heart.
The superior vena cava is a large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium. It is located in the upper right quadrant of the anterior heart and runs obliquely across the surface.
Coronary Arteries and Veins
The coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The left coronary artery arises from the aorta and gives rise to the left anterior descending artery and the circumflex artery. The right coronary artery arises from the aorta and gives rise to the right marginal artery and the posterior descending artery.
The anterior cardiac veins drain deoxygenated blood from the anterior surface of the heart. They include the great cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, and the small cardiac vein. These veins empty into the coronary sinus, which in turn empties into the right atrium.
Pericardial Structures
The pericardium is a two-layered sac that surrounds the heart. The fibrous pericardium is the outer layer and provides structural support. The serous pericardium is the inner layer and consists of two layers: the parietal pericardium, which lines the fibrous pericardium, and the visceral pericardium, which covers the heart.
The pericardial cavity is the space between the fibrous and serous pericardia. It contains a small amount of pericardial fluid, which lubricates the heart and reduces friction.
Key Questions Answered: Correctly Label The Following External Anatomy Of The Anterior Heart.
What are the major chambers of the anterior heart?
The major chambers of the anterior heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the function of the pulmonary artery?
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Where is the pericardium located?
The pericardium is located around the heart and is composed of two layers: the fibrous pericardium and the serous pericardium.