Icivics cabinet building answer key – Welcome to the realm of I-Civics Cabinet Building, where the answer key unlocks a world of civic engagement. Dive into this comprehensive guide as we explore the intricacies of cabinet roles, decision-making processes, and the profound impact on civic education.
Prepare to embark on a journey that will empower you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of government and public policy.
I-Civics Cabinet Building Background
I-Civics Cabinet Building is an online simulation that allows students to experience the process of building a presidential cabinet.
The simulation is designed to teach students about the different roles and responsibilities of cabinet members, as well as the challenges of appointing a diverse and qualified cabinet.
Educational Value of the Simulation
The simulation has a number of educational benefits, including:
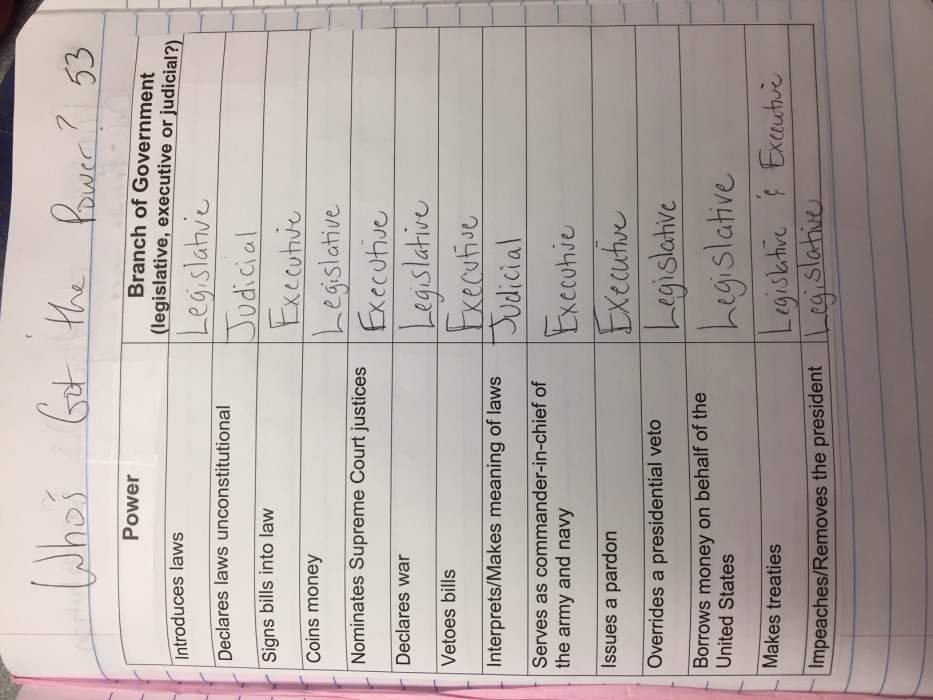
- Teaches students about the different roles and responsibilities of cabinet members
- Helps students understand the challenges of appointing a diverse and qualified cabinet
- Provides students with an opportunity to practice critical thinking and decision-making skills
- Encourages students to learn about the different branches of government and their respective roles
Cabinet Roles and Responsibilities
The I-Civics Cabinet Building simulation offers a diverse range of cabinet positions, each with distinct roles and responsibilities. These positions are designed to provide students with an immersive understanding of the inner workings of the executive branch of government.
Secretary of State
- Manages foreign policy and diplomatic relations.
- Coordinates with ambassadors and other foreign dignitaries.
- Negotiates and signs treaties and agreements.
Secretary of the Treasury
- Oversees the nation’s financial system and economic policies.
- Manages the federal budget and tax collection.
- Prints and distributes currency.
Secretary of Defense
- Leads the armed forces and oversees military operations.
- Advises the President on national security matters.
- Coordinates with foreign governments on defense and security issues.
Attorney General
- Heads the Department of Justice and oversees the enforcement of federal laws.
- Provides legal advice to the President and other government agencies.
- Represents the government in court cases.
Secretary of the Interior
- Manages public lands, natural resources, and Native American affairs.
- Oversees the National Park Service and other conservation programs.
- Protects endangered species and promotes environmental stewardship.
Secretary of Agriculture
- Supports the agricultural industry and promotes food security.
- Manages agricultural research and extension programs.
- Provides financial assistance to farmers and rural communities.
Secretary of Commerce
- Promotes economic growth and international trade.
- Oversees the Census Bureau and other economic data collection agencies.
- Supports businesses and entrepreneurs.
Secretary of Labor
- Enforces labor laws and promotes worker safety.
- Provides job training and employment services.
- Mediates labor disputes.
Secretary of Health and Human Services
- Oversees the nation’s healthcare system and social welfare programs.
- Manages Medicare, Medicaid, and other health insurance programs.
- Provides funding for medical research and public health initiatives.
Secretary of Education
- Leads the Department of Education and oversees federal education programs.
- Provides funding for public schools and universities.
- Sets educational standards and promotes student achievement.
Secretary of Housing and Urban Development
- Promotes affordable housing and community development.
- Provides financial assistance for homeownership and rental housing.
- Enforces fair housing laws.
Secretary of Transportation
- Oversees the nation’s transportation infrastructure, including roads, highways, and airports.
- Regulates the transportation industry and promotes safety.
- Invests in transportation research and development.
Secretary of Energy
- Develops and implements energy policies.
- Promotes clean energy and renewable resources.
- Manages nuclear energy and nuclear waste.
Secretary of Veterans Affairs
- Provides healthcare, benefits, and other services to veterans.
- Manages the Department of Veterans Affairs hospitals and clinics.
- Advocates for veterans’ rights and benefits.
Secretary of Homeland Security
- Leads the Department of Homeland Security and coordinates efforts to prevent terrorism and protect the nation from threats.
- Oversees border security, cybersecurity, and disaster response.
- Collaborates with state and local law enforcement agencies.
Decision-Making Process
The Cabinet decision-making process is a complex and multifaceted one that involves a variety of factors, including the President’s agenda, the input of Cabinet members, and the political climate. The process begins with the President identifying a policy issue that he or she wants to address.
The President then consults with Cabinet members to gather their input and advice on the issue. Cabinet members may present different perspectives and recommendations, and the President must weigh these views before making a decision.
Once the President has made a decision, he or she will issue a directive to the Cabinet. The Cabinet is then responsible for implementing the President’s directive. This may involve developing and implementing new policies, or it may involve overseeing the implementation of existing policies.
The Cabinet is also responsible for providing ongoing advice and support to the President on policy issues.
Collaboration and Compromise
The Cabinet decision-making process is a collaborative one. Cabinet members work together to develop and implement policies that they believe will benefit the country. However, it is not always possible to reach a consensus on every issue. When disagreements arise, Cabinet members must be willing to compromise in order to reach a decision that they can all support.
Challenges and Obstacles
Cabinet members may encounter various challenges and obstacles that can impact the decision-making process.
One challenge is the need to balance different perspectives and interests. Cabinet members come from diverse backgrounds and may have different priorities and values. This can lead to conflicts and disagreements, making it difficult to reach consensus on decisions.
Time Constraints
Another challenge is the time constraints under which cabinet members often operate. They are responsible for making decisions that have a significant impact on the country, and they must do so in a timely manner. This can lead to rushed decisions and a lack of thorough consideration of all the options.
Lack of Information
Cabinet members may also face challenges due to a lack of information. They may not have access to all the data they need to make informed decisions, which can lead to errors in judgment.
Political Pressure
Finally, cabinet members may face political pressure from the president, Congress, or the public. This pressure can make it difficult to make decisions that are in the best interests of the country, as opposed to the interests of the party or the individual politician.
Impact on Civic Education
I-Civics Cabinet Building significantly impacts civic education by providing students with an immersive and interactive learning experience that deepens their understanding of government and public policy.
The simulation immerses students in the roles and responsibilities of cabinet members, allowing them to experience firsthand the challenges and complexities of decision-making in a government setting. Through this hands-on approach, students develop a nuanced understanding of how government functions and the impact of public policy on society.
Fostering an Understanding of Government, Icivics cabinet building answer key
I-Civics Cabinet Building fosters an understanding of government by:
- Providing students with an immersive experience in the roles and responsibilities of cabinet members.
- Allowing students to witness the complexities of decision-making in a government setting.
- Encouraging students to research and analyze real-world policy issues.
Fostering an Understanding of Public Policy
I-Civics Cabinet Building fosters an understanding of public policy by:
- Exposing students to the different types of public policies.
- Teaching students how public policies are developed and implemented.
- Providing students with opportunities to analyze the impact of public policies on society.
Assessment and Evaluation
I-Civics Cabinet Building utilizes various methods to assess student learning and evaluate their progress.
One method is through online quizzes and assignments. These assessments are designed to test students’ knowledge of the material and their ability to apply it in practical scenarios.
Assessment Criteria and Rubrics
Assessment criteria and rubrics are used to evaluate student performance in I-Civics Cabinet Building. These criteria and rubrics are aligned with the learning objectives and provide clear expectations for students.
- Knowledge and understanding:This criterion assesses students’ grasp of the concepts and principles covered in the module.
- Critical thinking and analysis:This criterion evaluates students’ ability to analyze and evaluate information, identify key issues, and draw conclusions.
- Communication and collaboration:This criterion assesses students’ ability to communicate their ideas effectively, collaborate with others, and contribute to group discussions.
Integration into Curriculum
I-Civics Cabinet Building offers educators a versatile tool for enriching social studies curricula. Its interactive simulation allows students to engage with the complexities of government and decision-making, fostering critical thinking and civic literacy.
Lesson Plans and Activities
Incorporating I-Civics Cabinet Building into lesson plans can enhance student understanding of various social studies concepts:
- Branches of Government:Students can explore the roles and responsibilities of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, analyzing how they interact to form a system of checks and balances.
- Decision-Making Processes:The simulation challenges students to consider different perspectives, negotiate, and compromise to reach consensus on policy decisions, mirroring real-world political processes.
- Civic Engagement:By actively participating in the simulation, students develop a deeper understanding of the importance of civic participation and the role of citizens in shaping public policy.
Resources for Educators: Icivics Cabinet Building Answer Key
I-Civics Cabinet Building offers a wealth of resources to support educators in their implementation of this engaging and effective civic education tool.
These resources include lesson plans, videos, interactive simulations, and professional development opportunities designed to help educators:
Lesson Plans
- Aligned with national and state standards, these lesson plans provide step-by-step instructions for incorporating I-Civics Cabinet Building into the classroom.
- Each lesson plan includes learning objectives, materials, activities, and assessment suggestions.
Videos
- Engaging videos introduce students to the concepts and processes of cabinet government.
- These videos can be used as a starting point for discussions or as a review of key concepts.
Interactive Simulations
- Interactive simulations allow students to experience the challenges and responsibilities of cabinet members firsthand.
- These simulations provide a hands-on learning experience that helps students understand the complexities of decision-making in government.
Professional Development Opportunities
- I-Civics offers professional development workshops and online courses for educators who want to learn more about I-Civics Cabinet Building.
- These opportunities provide educators with the knowledge and skills they need to effectively use this resource in their classrooms.
With its comprehensive suite of resources, I-Civics Cabinet Building empowers educators to provide their students with a rich and engaging civic education experience.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of the I-Civics Cabinet Building simulation?
The simulation aims to provide students with an immersive experience in cabinet decision-making, fostering an understanding of government processes and the challenges of public policy.
How does the decision-making process work in the simulation?
Cabinet members collaborate and debate, considering diverse perspectives and seeking consensus through compromise and negotiation.
What are the key challenges faced by cabinet members in the simulation?
Challenges include balancing competing interests, navigating political dynamics, and making decisions under time constraints and with limited information.